Course Introduction
Course Introduction
Core Standards of the Course
Strand 1
BRANDING - Students will be able to define Marketing and Digital Marketing and identify trends in the Digital Marketing Industry.
Standard 1
BASICS OF MARKETING - Students will be able to demonstrate a basic understanding of Marketing and Digital Marketing
-
Compare the differences between Digital Marketing & Traditional Marketing
-
Explain how each component of the marketing mix contributes to successful marketing.
-
Explore marketing in the 21st century
-
Introduce the Marketing mix
- Product: a good or service.
- Price: amount of money requested or exchanged for a product, should cover expenses and allow for a profit
- Place: activities involved in getting a product or service to the end user, may include: shipping, ordering processing, inventory storage, and stocking of goods. Describe that place can be both a physical location or online site.
- Promotion: process of communication with customers and potential customers to inform, persuade, and remind about products, their price, and where they can be purchased
-
Review the Promotional Mix
- Advertising: paid non-personal communication usually targeted at large numbers of potential customers.
- Public Relations: is a strategic communication process that builds mutually beneficial relationships for a company and the public or its markets.
- Selling: is a process of persuasion to get potential customers to take action.
- Sales Promotion: is a marketing strategy where the product is promoted using short-term attractive initiatives to stimulate its demand and increase its sales.
Standard 2
BRANDING - Students will understand the concept of a Branding identity and Brand Positioning, Brand Persona
-
Define branding as a company name, logo, the design, or a combination used to identify and differentiate itself from the competition. Branding should connect with customers emotionally and motivate them to buy.
-
Explain the importance of creating a brand experience: the essence of what you represent, a company’s positioning, and the experience you are trying to deliver at each interaction with your customers.
-
Unique Value Proposition: the core benefit or solution that differentiates your product or service from the competition.
-
Brand Recognition: when people are able to recognize a brand through visual or auditory cues such as logos, slogans, packaging, colors, or jingles rather than being explicitly exposed to a company’s name.
-
Brand Value:
-
Brand Loyalty: When consumers continue buying the same brand of goods rather than competing brands.
-
Brand Style Guide
-
CX (Customer Experience)
- Touchpoints any encounter where customers and business engage to exchange information, provide service, or handle transactions. Your brand’s points of customer contact, from start to finish.
- For example, customers may find your business online or in an ad, see ratings and reviews, visit your website, shop at your retail store, or contact your customer service.
- Favicon: A bookmark icon or tab icon associated with a website
- Touchpoints any encounter where customers and business engage to exchange information, provide service, or handle transactions. Your brand’s points of customer contact, from start to finish.
Standard 3
TARGET MARKET - Students will understand how to determine target market through understanding the four components of a Buyer’s Persona
-
Buyers Persona: Representation of your ideal customers based on data and research
- Describe how businesses determine their target market using Marketing
- Segmentation: which is the process of dividing a market of potential customers into specific groups based on different characteristics.
- Demographics: Who? (Personal characteristics such as Age, Gender, Income Level, Education Level, Race, Ethnicity)
- Geographics/Location: Where? (Segmentation based on where people live such as Natural or Political Boundaries, Climate, Cultural influences, and Customs)
- Psychographics/Interests: Why? (Involves grouping people with similar lifestyles, as well as shared attitudes, values, and opinions such as Activities, Attitudes, Personality & Values)
- Behavioral: How? (Looking at the benefits desired by consumers such as shopping patterns, usage rate, benefits--and not just the physical characteristics of a product)
- Segmentation: which is the process of dividing a market of potential customers into specific groups based on different characteristics.
- Challenges/Pain Points: a specific problem that prospective customers of your business are experiencing.
- Goals/Motivations
- Interests/Hobbies
- Describe how businesses determine their target market using Marketing
Standard 4
Students will distinguish the intellectual property protections available to brands.
Performance Skills (Choose one):
-
Research a business and identify their brand, logo, and slogan and/ or digital content. Describe how this business differentiated itself through branding.
-
Create a brand style guide using an online digital media program.
Strand 2
CONTENT CREATION - Students will understand the role and importance of content creation in digital marketing.
Standard 1
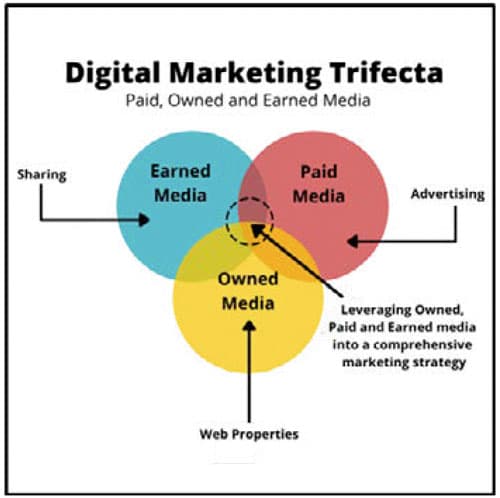
Students will understand the history, role and importance of content marketing in digital marketing. Students will be able to explain the three types of digital content, Paid, Owned, and Earned and how they contribute to the Digital Marketing Trifecta.
-
Content Marketing: is a marketing technique of creating and sharing content to attract a target audience to help them convert to customers.
-
Owned Media: is any content owned and controlled by a brand, such as a content posted on a blog, website or social media channel.
-
Earned Media: is any material written about a business that the business hasn’t paid for or created themselves.
-
Students will understand the difference between creating their own content and taking advantage of trending content and hashtags
-
Paid Media: is marketing that you pay for and includes PPC advertising, branded content, and display ads.
-
Digital Marketing Trifecta: is leveraging Owned, Earned and Paid content and media into a successful marketing strategy.
Standard 2
Students will understand many different types of content marketing used in digital marketing today, as well as the difference between creating their own content and taking advantage of trending content and hashtags.
-
Identify and define the types of content available to digital marketers.
- Blogs: consist of posts which present engaging stories in an information style. Examples include food, travel, fashion, politics, DIY and lifestyle blogs.
- Interactive Content: like surveys, polls, and quizzes requires and encourages users to actively engage with content, rather than passively consume it. It can be used to drive engagement time online.
- Videos/Photos: are types of visual content in marketing.
- Memes: are typically a humorous image, video, piece of text, etc., that is copied (often with slight variations) and spread rapidly by internet users.
- Gifs: (Graphics Interchange Format) are an image type (like jpeg, png, pdf) used to create animated files.
- Hashtags: are used before relevant content as a way to connect social media content to a specific topic, event, theme or conversation. Hashtags tie public conversations from all different users into a single stream.
- Emails: are messages distributed by electronic means from one computer user to one or more recipients via a network.
- Podcast: is a digital audio file made available on the internet for downloading to a computer or mobile device, typically available as a series.
- Infographics: are graphic visual representations of information, data, or knowledge intended to present information quickly and clearly.
-
Explain the difference between marketers creating their own content versus capitalizing on viral content created by others.
- Viral Content: is online content that achieves a high level of awareness due to shares and exposure on social media networks.
- Trendjacking: commonly known as newsjacking, refers to brands who take advantage of current trends happening on social media instead of creating their own viral content. Search industry leaders for trends research.
Standard 3
Students will define the stages of a digital consumer’s buyer’s journey and their importance in a customer’s conversion process.
-
Contrast the stages buyers go through to become aware of, consider and evaluate, and decide to purchase a new product or service.
- Buyer’s Journey: is the process by which every potential customer decides on a product or service. In general, every buyer follows three main steps in the buying process before becoming a customer: awareness, consideration, and decision.
- Awareness Phase: When a potential buyer becomes aware that they have a problem that needs resolution.
- Consideration Phase: When a buyer identifies and evaluates their options in an effort to determine a solution to their problem.
- Decision Phase: When a buyer makes their final purchase decision.
- Conversion: occurs when a visitor to your website completes a desired goal, such as filling out a form or making a purchase.
- Buyer’s Journey: is the process by which every potential customer decides on a product or service. In general, every buyer follows three main steps in the buying process before becoming a customer: awareness, consideration, and decision.
-
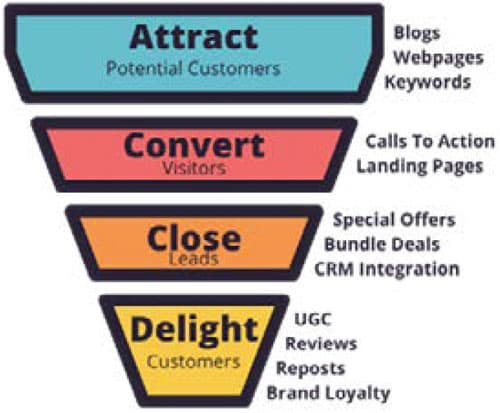
Explain the role of digital marketing funnels and customer relationships within the digital marketing industry.
Performance Skill (Choose one):
- Students will conduct a conduct a content audit of a website or digital marketing content on a digital platform using performance metrics to determine:
- Which content to keep as-is
- Which content to improve
- Which content to remove or consolidate
- Students will analyze digital marketing content that went viral and explain their analysis of why/how the content went viral.
- Students will analyze and explain a firm’s Digital Marketing and or Sales Funnel or buyer’s journey.
Strand 3
CONTENT OPTIMIZATION - Students will investigate the optimization of digital content by providing essential text and visual data to maximize target audience reach.
Standard 1
SEO - Students will understand how content is deployed and distributed to improve consumer trust and quality of a domain and search engine optimization (SEO)
-
SEO - is the art of increasing the quantity and quality of traffic to your website through organic search engine results when keywords are searched.
-
Web Crawlers - also known as a spider, is a type of bot that’s operated by search engines like Google and Bing. Their purpose is to index the content of websites all across the Internet so that those web sites can appear in search engine results. That index is then fed through an algorithm that tries to match all that data with a query (question).
-
Students will examine how the Search engine results and algorithm implementation provide qualitative and targeted results to search engine queries.
- Search Engine Result Page (SERP) - The page that a search engine returns after a user submits a search query. Search engine results pages include paid search, PPC ads and organic results.
- Page Rank - a rank based on algorithms used by a search engine to determine the most popular/appropriate/ best website to answer the question you’ve searched for:
- Trust/Authority
- Quality
- Backlinks - also known as “inbound links”, “incoming links” are links from one website to a page on another website.
- Keywords
- Search Engine Algorithms - ranking systems used by search engines to sort website data based on relevancy and quality instead of publish time.
- Social Media Algorithms - Social media algorithms are a way of sorting posts in a users’ feed based on relevancy instead of publish time.
Standard 2
Students will evaluate the use of using qualifiable data and measurement in guiding digital marketing campaigns, driving conversion and increasing brand awareness.
-
Metrics - A method of measuring something.
-
Key Performance Indicator (KPI) - A metric used to evaluate the success of an organization to meet a goal.
-
Awareness KPI
-
Engagement KPI
-
Conversion KPI
-
Average Transaction Value (x) Purchase Frequency (x) Years of Relationship = CLV
Standard 3
Students will explore data measurement as it relates to the collection, reporting, and analysis of website data. Students will understand how analytics drives digital marketing goals, strategies and improves user’s experiences.
-
Analytics - The evaluation of digital marketing strategies using a website or digital advertising KPIs.
- Analytics Goals - measure how often users complete specific actions on a website. A goal conversion takes place when your visitors complete the action you are tracking—for example, make a purchase, add a product to cart, or sign up for a newsletter.
- Audience, Acquisition, and Behavior Reports
- Insights into buyer persona
- Data Driven Decisions
Performance Skills (Choose one)
- Conduct an SEO Audit using a free digital tool
- Research a social platform to determine how algorithms affect a user’s feed
Strand 4
CONTENT DISTRIBUTION - Students will understand the importance of content distribution to online audiences in multiple media formats across multiple digital channels.
Standard 1
Students will understand owned content distribution essentials and trends.
-
Students can explain the best practices for effective use of websites as owned media channels.
- Mobile/Desktop friendly website design
- Clear website navigation
- The implementation of CTAs (Call To Action) - Content intended to induce a viewer to perform a specific act. (e.g. “Buy Now or Click Here”). CTAs redirect to specific landing pages.
- Landing Pages are where a visitor “lands” after they click on a CTA (link in an email, or ads from Google, Bing, YouTube, Facebook, Instagram, Twitter, or similar places on the web.)
- Website security
- SSL Certificate (Secure Socket Layer) - A standard security feature which establishes an encrypted link between a website and a customer. It is often identified by a lock icon.
- Social media integration
- Clear website branding
-
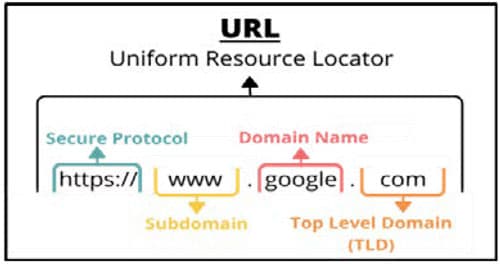
Students will identify how website internet domain names are organized by top-level domains (TLD)
- URL (Uniform Resource Locator) is a location or address identifying where documents can be found on the internet.
- HTTPS:// - Hypertext transfer protocol secure (HTTPS) is the secure version of HTTP, which is the primary protocol used to send data between a web browser and a website. HTTPS is encrypted in order to increase security of data transfer.
- TLD (Top Level Domain) are the letters at the end of a website. They typically tell a story about the domain name associated with it, such as the geographical area it was created in, its purpose, or the organization that owns it.
- A Domain Name is a website name. In simple terms, if your website was a house, then your domain name will be its address.
-
Students will recognize the impact of content distribution on social media channels.
- Consistent branding across all digital channels and touchpoints.
- Correct content sizing for each digital channel and mobile application
- Consumer Data Privacy Laws - Emerging legislation which allows users to opt out of having their data collected and sold. Users may also see what data companies have collected about them, and correct or delete it.
Standard 2
Students will understand e-commerce site essentials and trends in online commerce.
-
Students can understand the difference between the 4 main types of e-commerce.
-
Students can identify website features and metrics which can be used to measure the success of an ecommerce store and electronic shopping carts.
-
Cart Abandonment Rate - a term associated with the use of virtual shopping carts when the transaction is not completed.
-
Net Promoter Score (NPS) - A calculation that measures the likelihood of a customer recommending your business. % of promoters - % of detractors
Standard 3
Students can identify the components of paid content distribution and how it can be effectively used to promote content using various platforms and networks.
-
Students can explain how Owned and Earned content can become Paid content.
-
Students will compare and contrast organic and paid advertising promotion strategies.
- Organic Ads - Ads that get your customers to come to you naturally over time, rather than ‘artificially’ via paid links.
Paid Ads - Promoted ads placed on digital media platforms
- Pay Per Click Advertising (PPC) - Internet advertising used to direct traffic to websites, in which an advertiser pays a publisher (typically a website owner or a network of websites) when the ad is clicked.
- Cost Per Click (CPC) - refers to the actual price you pay for each click in your pay-per-click (PPC) marketing campaigns.
- Click Through Rate (CTR) - The percentage of people visiting a web page who click a link to a PPC advertisement.
- Affiliate Marketing - The process of earning a commission for marketing anothers person’s products or services. (e.g. bloggers)
- Cost Per Conversion - a metric used to identify how much it actually costs a web advertiser to acquire each real customer - one that actually makes a purchase.
- Pay Per Click Advertising (PPC) - Internet advertising used to direct traffic to websites, in which an advertiser pays a publisher (typically a website owner or a network of websites) when the ad is clicked.
-
Students can learn to define both negative and positive keywords for ads, to optimize when ads should appear.
-
Students will be able to evaluate the need to retarget or remarket and test ad campaigns to reach their target market.
- Retargeting/Remarketing - is a way to connect with people who previously interacted with your website or mobile app through the use of ad networks and their partner websites.
- A/B Testing - is a research method where two or more variants of a page are shown to users at random, and statistical analysis is used to determine which variation performs better for a given conversion goal.
-
Students will define Search Ads as text ads which are displayed among search results on a Search Engine Results Page (SERP).
-
Students will understand the various types of Display Ads as types of graphic ads placed on websites, social media channels or apps.
- Banner Ads, also known as the most common type of display ad, use imagery to attract attention with the goal of driving traffic to from a host website to an advertiser’s website.
- Static Ads - Ads which have no movement
- Wallpaper Ads are ads which automatically insert themselves in the full background of the page, commonly known as a “takeover.”
- Pop Up Ads are a highly effective form of online advertising in which a small window suddenly appears on a webpage.
- Banner Ads, also known as the most common type of display ad, use imagery to attract attention with the goal of driving traffic to from a host website to an advertiser’s website.
-
Students will understand the importance of Promotional Video as a short film that highlights a business or influencer and drives traffic toa website or social media channel.
Performance Skills (Choose one)
- Research data privacy laws and how they can affect the implementation of paid advertising.
- Analyze an e-commerce site for its effectiveness including: website navigation, landing pages, security, social media integration, website branding, CTA and customer reviews.
Strand 5
Social Media Marketing - Students will be able to differentiate between the various social media platforms and their unique advantages to a marketing campaign. Students can connect how social media marketing has the ability to aid traditional marketing in market research, promotion, and engagement.
Standard 1
Students will be able to compare and identify advantages and disadvantages of using social media for marketing.
-
Define Digital Footprint as a trail of data you create while using the Internet. It includes the websites you visit, emails you send, and information you submit to online services and recognize its characteristic of permanence.
-
Explain the cause and effect of various internet safety precautions, (such as hackers using social media profiles to figure out passwords), or lack thereof.
-
Summarize advantages to using social media as an effective inbound marketing strategy in comparison to traditional marketing approaches. Some examples are Product Promotion, Sales, Jobs, Low Cost Research, and Wide distribution.
Standard 2
Identify and describe how social media is used for marketing research, promotion, customer service, brand building, sales, and engagement
-
Define these terms relating to tools, strategies and techniques used in social media for marketing:
- Social Monitoring is the process of tracking content on digital content as a way to find out what people are saying about your brand, competitors, industry, and products or services.
- Customer Interaction is a communication between a customer and a company.
- Every interaction with a customer is a chance to connect with them, delight them, and increase their retention and advocacy.
- Product recommendations
- Gaining Buyer Persona Insights (Include: Demographics, Geographics, Best Engagement Times)
- Profile Management software is available to be able to manage social media accounts and all your personas.
Standard 3
Students will compare and contrast the most popular social media platforms and their advantages and disadvantages for various marketing outcomes - Facebook, Twitter, Instagram, Pinterest, Youtube, TikTok, Linkedin
-
Identify the most effective content types for each unique platform and understand the role that each platform plays in the marketing of products and services.
-
Explore various forms of content that are most effective on current social media platforms. Such as Stories, Reels, Images, IGTV, Lives, Blog Posts, Infographics, Memes, User Generated Content , Podcasts, or VR Content
-
Describe and categorize typical users of each social media platform
- Investigate different platform engagement strategies
- Which content is best for each platform
- How to sell on differing social platforms
- Understand different Platform Algorithms
- AI/Machine Learning
- Identify platform usage trends for each platform
- Demographics of each platform
- Most effective posts per day/week for each platform
- Investigate different platform engagement strategies
Strand 6
Public Relations and Outreach - Students will analyze the opportunities available to maintain positive customer relationships through producing timely, relevant and shareable content.
Standard 1
Students will identify current trends in automated marketing strategies as a means to efficiently maintain positive customer relationships and increase conversion rates.
-
Automated Marketing - Software and technologies used to more effectively market on multiple online channels and automate repetitive tasks.
-
Social Media Automation - Using paid or free software and tools to automate things like scheduling, posting and sharing content on Facebook, Twitter, and other channels.
-
CRM Software (Customer Relationship Management) - is any tool, strategy, or process that helps businesses better organize and access customer data.
Standard 2
Students will understand why businesses need to utilize mobile and web apps to interact with customers, as well as the advantages and disadvantages of each type of app.
-
Web App - Web apps are accessed via an internet browser and adapt to whichever device you’re viewing them on. They don’t need to be downloaded or installed.
-
Mobile App - Mobile apps are built for a specific platform, such as iOS for the Apple iPhone or Android for a Samsung device. They are downloaded and installed via an app store and have access to system resources, such as GPS and the camera function.
-
Students will explore the different benefits and applications of mobile app technology.
- Push Notifications - similar to text messages, push notifications are clickable messages that pop up on mobile devices and used by app publishers to gain traffic.
- Customer Loyalty Programs / Rewards
- Real Time Marketing Strategies - focus on current, relevant trends and immediate feedback from customers.
- Location Based Marketing - using a mobile devices location to alert the device’s owner about an offering from a nearby business.
Standard 3
Students will understand the process and benefits of pitching a company’s products and/or services to those with a platform (ex. bloggers, influencers, journalists) to get exposure and press coverage.
-
PR (Public Relations) - strategies intended to help a business cultivate a positive reputation with the public through various unpaid or earned communications.
-
Cross Promotion - the cooperative marketing by two or more companies of each other’s products or services.
Standard 4
Students will understand the parts of a digital marketing campaign and the importance of documenting your plan for team communication and financial investment.
-
Executive Summary
-
Description of Event, Product, or Service
-
Campaign Objectives
-
Campaign Target Market
-
Campaign Activities & Schedule
-
Budget
-
Key Metrics
Performance Skills (Choose one)
- Create a press release for a student generated website or innovative business idea and include the following key components:
- Header
- Description (Subject line)
- Introduction
- Screenshots/Images (Product/app/website)
- Body
- Key facts/quotes
- Website URL and Info
- About Your Company
- Media Contact Details
- Have students generate and mock up a new concept for a social media mobile app.
Strand 7
Careers and CTE Pathways - Students will understand the Utah Marketing Pathway and how it can help students to find careers in digital marketing
Standard 1
Identify potential careers in data analytics and digital marketing. Examples: Digital Marketer, Social Media Specialist, Digital Advertising Specialist, Content Creator, Paid Media Specialist, and Marketing Manager.
-
Determine personality traits that support these types of jobs.
-
Understand CTE High School to College and Career Pathways that relate to advertising careers and other classes offered related to these Pathways.
- Describe the Utah pathway(s) that Digital marketing is currently included in.
- Utah CTE Pathways
- UTech Utah technical college network for technical colleges and the digital marketing programs that exist locally. Explore what opportunities are available for Utah high school Seniors.
- Identify secondary certifications and/or degrees needed for these types of careers.
- USHE Utah System of Higher Education. Highlight the current BS or BA opportunities in Social Media Marketing, Digital Marketing, or Marketing
- Students can gain credentials and show experience by seeking out certifications online such as; Google Ads, Facebook Ads, Hubspot.com, Hootsuite.com and stukent.com.
- Describe the Utah pathway(s) that Digital marketing is currently included in.
Standard 2
Personal Digital Marketing - Students will understand their own online presence and personal brand.
-
Students will understand the importance of personal marketing pertaining to digital marketing career opportunities. What is your brand? How would you describe yourself? Do your social media accounts give the impression that you want them to?
-
Explain the use of Social media as a common screening practice for future college and career opportunities
Performance Skills (Choose one)
- Have students conduct a self audit of their personal social media accounts. Are there posts, comments, images, or any groups that you feel wouldn’t recommend them to a future employer? After they have gone through their accounts, have them write an essay on what they learned about their own social media persona. Would they hire themselves if they had only their social media to look at?
- Have students research a digital marketing career that is currently listed on one of the many job posting websites. Then report on the required education, experience, certifications and the jobs potential pay and demand today.
- Communication
- Problem Solving
- Teamwork
- Critical Thinking
- Dependability
- Accountability
- Legal Requirements/expectations
- Data interpretation
 http://www.uen.org - in partnership with Utah State Board of Education
(USBE) and Utah System of Higher Education
(USHE). Send questions or comments to USBE
Specialist -
Racheal
Routt
and see the CTE/Business, Finance and Marketing website. For
general questions about Utah's Core Standards contact the Director
-
THALEA
LONGHURST.
These materials have been produced by and for the teachers of the
State of Utah. Copies of these materials may be freely reproduced
for teacher and classroom use. When distributing these materials,
credit should be given to Utah State Board of Education. These
materials may not be published, in whole or part, or in any other
format, without the written permission of the Utah State Board of
Education, 250 East 500 South, PO Box 144200, Salt Lake City, Utah
84114-4200.
http://www.uen.org - in partnership with Utah State Board of Education
(USBE) and Utah System of Higher Education
(USHE). Send questions or comments to USBE
Specialist -
Racheal
Routt
and see the CTE/Business, Finance and Marketing website. For
general questions about Utah's Core Standards contact the Director
-
THALEA
LONGHURST.
These materials have been produced by and for the teachers of the
State of Utah. Copies of these materials may be freely reproduced
for teacher and classroom use. When distributing these materials,
credit should be given to Utah State Board of Education. These
materials may not be published, in whole or part, or in any other
format, without the written permission of the Utah State Board of
Education, 250 East 500 South, PO Box 144200, Salt Lake City, Utah
84114-4200.


 UTAH EDUCATION NETWORK
UTAH EDUCATION NETWORK

 Justin
Justin Braxton
Braxton Dani
Dani Kayla
Kayla Katie
Katie Lora
Lora Rob
Rob Val
Val